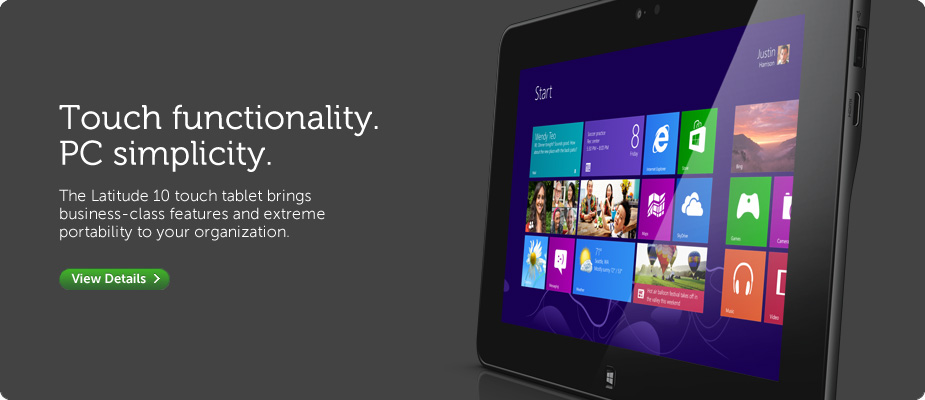
In the last couple of weeks I’ve received two advertising flyers from the folks at Dell. As usual, both were pretty flashy print jobs featuring high quality color photography on slick paper. One of the brochures was aimed at business customers, the other at consumers.
Christine Hall has been a journalist since 1971. In 2001, she began writing a weekly consumer computer column and started covering Linux and FOSS in 2002 after making the switch to GNU/Linux. Follow her on Twitter: @BrideOfLinux